


Are you familiar with the popular iconography of the saint whose feast day falls on April 23? If you’ve ever been to an English pub, you probably are, even if you didn’t realize it! According to medieval legend, Saint George of Cappadocia was the third-century saint and martyr who slew a dragon. Usually, George is represented as a knight mounted on a horse. Sometimes shown carrying a cross-inscribed shield, his red and white armorial attribute, he thrusts his lance into the jaws of the dragon under his horse’s hooves.
George’s heroic posture was modeled on the iconography of other saints and mythological figures. Theodore Tyro and Demetrius of Thessalonica, for example, also slew beasts in the name of vanquishing evil. Carrying talismanic or protective power for people threatened by worldly dangers, dragon-slayer images decorated many small, portable objects, including ampullae, lamps, carved gems and small plaques from the late antique, Byzantine, and Coptic worlds.1 Building on narratives of his heroism, tales of George’s life and deeds spread throughout medieval Europe with Crusaders returning from the East. By the high Middle Ages, the Golden Legend, a compilation of saints’ lives by Jacobus de Voragine, fleshed out the life of George with a rescue narrative of a king’s daughter and inspired numerous visual representations in different media.2
Depictions of the rescue legend, which follow standard iconography for George’s slaying of the dragon, often insert the princess as a minor character of relative insignificance. But is she insignificant? Traditionally identified as a third or fourth century Komnenian princess of Trebizond, she is sometimes named Sabra or Cleodolinda (or Cleolinda, Cleudolinda) (Fig. 1). According to the legend, the princess was weeping profusely, anticipating her certain death as the next human sacrifice to the dragon, when George arrived at a town called Silene in Libya. He pledged to help her, and he rode toward the dragon with his sword drawn.3 In swift succession, George pierced the dragon and the princess bound her girdle around the beast’s neck. She led it back to the townspeople alive which brought about the people’s mass conversion to Christianity.

In some earlier depictions of the legend, the princess appears with prominence, including on a Romanesque capital from a monastery in Saint-Pons-de-Thomières now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art. On the capital face, the princess wears a long dress, props one hand on her hip, and extends a flower toward George (Fig. 2). Around the other side, George kneels behind his shield, trailing a coiled serpent that approaches the princess from behind. Her thank offering to George in the midst of his attack on the dragon suggests that there will be a good outcome despite the violence surrounding her.

In another Romanesque capital from the abbey of Saint-Pierre of Airvault in Poitou, the princess stands behind George, although he rides away from her, effectively separating her from the dragon’s reach (Fig. 3). With George exiting left, the princess becomes a key figure of interest to viewers gazing upward at the capital. Here, she maintains a stoic stance, and, in ironic juxtaposition with the nearby head of a menacing grotesque, her arms are crossed over her body in a way that suggests patience and perseverance in the face of danger.

By the late fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, the iconography of the princess and her role in George’s slaying of the dragon were handled with more flexibility, especially in manuscript illumination.5 Some examples, such as the Hungarian Angevin Legendary, illustrate the narrative more literally, showing the princess tethering the dragon or leading it away by its makeshift leash (Fig. 4). In this variant of her iconography, the Princess of Trebizond is actively engaged with George’s feat and secures the dragon in one forceful pull.

At George’s suffrage in illuminated prayerbooks, especially in Books of Hours, the princess often appears behind the slaying scene, kneeling in prayer, and protected a distance.6 But in some of these late medieval depictions, she tends a flock of sheep, sometimes holding one sheep on a lead, or she simply raises her hands in surprise at George’s victory (Fig. 5).7
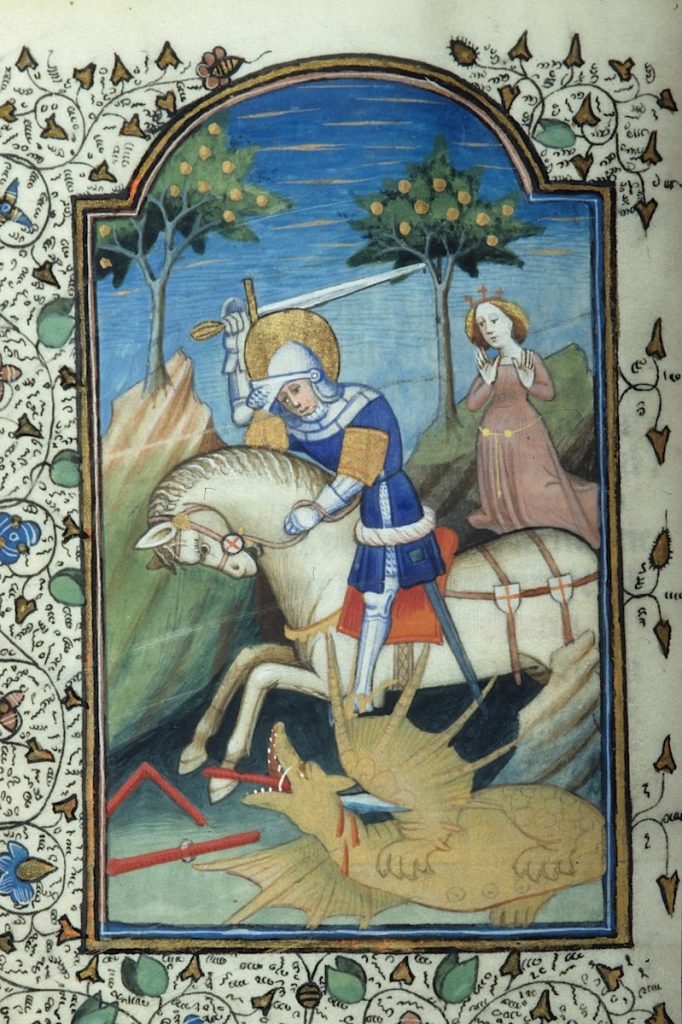

In all these images, the princess functions as more than a mere attribute of George. Instead, she is actively reimagined as part of the narrative. Artists creatively customized their images of Georgian legend to not only explore the princess’s instrumental role in her rescue but to highlight her intercessory function in saving the townspeople–in a literal sense and by their newfound faith. Whether showing her as prayerful, gracious, surprised, or tethering the dragon, the iconography of the princess offers a versatile model of female agency, one that likely inspired her viewers.
We can find echoes of such rescue narratives in other ages and media. If you have played the classic Super Mario Bros. video game, then you know the game’s mission: rescue Princess Peach! As aficionados know, the eighth and final world of the game culminated in an underground battle with Bowser, the hammer-hurling, spiky-shelled antagonist (Fig. 6). If you hurled enough fireballs back at Bowser, he overturned and descended into an abyss off screen, allowing Mario to advance over the bridge and reach the princess on the other side. Much like the Princess of Trebizond, Princess Peach had to be rescued, and she, too, has been reimagined over time: her characterization within the Nintendo empire of games and films eventually evolved from damsel in a dungeon to a fighter in her own right.8

You can still find the iconography of George slaying the dragon in the modern world, often in a reduced composition of equestrian, saint, and dragon. Once you know what you’re looking for, you’ll spot George in any number of settings, especially on pub signs like the one on my local haunt when I was a grad student in London (Fig. 7). Whether under his sign or not, those who cheer to Saint George today would do well to remember this: once upon a time, a princess filled with purposeful character also conquered a beast.
Thank You, Saint George! Your Quest is Over.
Appendix
The Index subject files provide a starting point to locate examples of the Princess of Trebizond in the six works of art:
The Index of Medieval Art is pleased to continue a series of blog posts that delve into the history of the organization through interviews with senior scholars in the field of art history. The “Guest Book Series” takes its name from the Index guest books, which have been signed by hundreds of art historians who have consulted the Index files over the past century. We’ve enjoyed reading their recollections and warmly thank Lucy Freeman Sandler, Professor Emerita, Institute of Fine Arts of New York University, and Index friend for her time and responses.
Please tell us a little about yourself and your work. Where did you study? What inspired you to become a medievalist?
I began to study painting at Queens College but my first undergraduate art history course focused my interest in a new direction, and, inspired by a charismatic medievalist, Frances Godwin, I decided to study the art of the Middle Ages on the graduate level. On Prof. Godwin’s advice I applied to and was accepted at Columbia University and took courses with Meyer Schapiro, a formative intellectual experience, and then with John Plummer, who was then himself completing a Ph.D. with Schapiro. It was Plummer’s course, called “Gothic Painting,” which was primarily about illuminated manuscripts, in which I “discovered” marginal illustrations, a topic that became the subject of my master’s thesis. For my own Ph.D. I transferred to the Institute of Fine Arts of New York University (they generously awarded me a scholarship), eventually completing a dissertation on the Psalter of Robert de Lisle (London, British Library, Arundel MS 83).

When was your first visit to the Index in Princeton? Where was the Index located? With whom did you work there? Do you remember anything especially interesting about your visit?
I cannot remember the date of my first visit to the Index, which Index records indicate was 1961, during the time I was working on my dissertation. I have certainly used the Index many times since, and have known all its directors since Rosalie Green, although, to my regret, I did not meet her.

Have you made any great iconographic discoveries related to your research using the Index? Have you used the Index for teaching as well as for research?
I remember at least one visit, probably sometime between 1961 and 1964, when I was trying to determine the date during the Gothic period at which the crossed feet of the Crucified Christ changed position. I must have looked at hundreds of photos of every late thirteenth and fourteenth century Crucifixion at the Index. I can’t say that I came to any definitive conclusion but I certainly learned a lot about Crucifixion representations. I have found the online version of the Index invaluable, especially in connection with my latest book, Penned & Painted: The Art and Meaning of Books in Medieval and Renaissance Manuscripts (London: British Library, 2022), for which I did much of the research during Covid.

Have you attended or presented at an Index conference? Which conferences were particularly memorable or helpful to your work?
I have attended quite a few Index conferences and have spoken at several, including “The Weingarten Office Lectionary and Passionale in New York and St. Petersburg,” in Romanesque Art and Thought in the Twelfth Century in Honor of Walter Cahn (October 2006); “One Hundred and Fifty Years of Study of the Illuminated Book in England: The Bohun Manuscripts from the Nineteenth Century to the Present,” in Gothic Art & Thought in the Middle Ages: A Conference in Honor of Willibald Sauerländer (March 2009); “The Bohun Women and Manuscript Patronage in Fourteenth Century England,” in Medieval Patronage: Patronage, Power and Agency in Medieval Art (October 2012); and “Princeton Garrett MS 35 and Homeless English Gothic Manuscripts,” in Manuscripta Illuminata: Approaches to Understanding Medieval & Renaissance Manuscripts (October 2013). All these were subsequently published under the editorship of Colum Hourihane. I also contributed a tribute to John Plummer: “John Plummer: A Reminiscence,” in Between the Picture and the Word: Manuscript Studies from the Index of Christian Art, ed. C. Hourihane (University Park, PA, 2005), 9–11.
Do you have any observations about the evolution of the field of medieval iconographic studies over the last three decades?
As co-editor of the Index-based Studies in Iconography, from 2009–2015, I hoped to serve the mission of the journal, as it has continued to the present, to publish “innovative work on the meaning of images from the medieval world broadly construed.”
Thank you, Lucy! As the home for Studies in Iconography we’re committed to publishing innovative work in iconographic studies, and we’re grateful for your invaluable contributions to the Index over so many years.
The Index of Medieval Art is pleased to continue a series of blog posts that delve into the history of the organization through interviews with senior scholars in the field of art history. The “Guest Book Series” takes its name from the Index guest books, which have been signed by hundreds of art historians who have consulted the Index files over the past century. We’ve enjoyed reading their recollections, and we warmly thank Herbert Kessler, Professor Emeritus at Johns Hopkins University and Index friend, for his time and responses.
Please tell us a little about yourself and your work. Where did you study? What inspired you to become a medievalist?
After studying medieval art as an undergraduate at the University of Chicago, I completed the MFA and Ph.D. at Princeton. At UC, Margaret Rickert had inspired me to become a medievalist; she was also Rosalie B. Green’s Doktormutter, so Rosalie and I had a special bond from the start. I continued to use the Index at Dumbarton Oaks when I was a Fellow there in 1965–66 and then, again, when I returned to Princeton as a Fellow at the Institute for Advanced Study in 1969–70.

When was your first visit to the Index in Princeton? Where was the Index located? With whom did you work there? Do you remember anything especially interesting about your visit?
RBG1 oriented all new graduate students, so 1961. The Index was then in the Neo-Gothic Cram wing of the original McCormick Hall. Graduate students had keys and used it steadily, especially as a picture resource. The Index staff felt under-appreciated and with good cause: though RBG and Isa Ragusa were distinguished and consistently professional and helpful they knew that the faculty did not respect them as scholars. When I was being recruited to the University of Chicago faculty in 1965, the Dean offered to acquire a copy of the Index for me (because William Heckscher, who had been offered the position earlier, had asked for one), but nothing came of that. As computers were evolving in the 1980s, the Getty Center hired two young persons to recommend ways in which the Index might be digitized. Things did not go well, and I was sent (from Johns Hopkins) to reconcile the Index staff with the Getty interlopers. During the discussions, we all realized how the new technology might allow the Index to be modified in ways better to serve other disciplines, especially e.g. by refining types of musical instruments, botanical and zoological species, or agricultural implements.
Have you made any great iconographic discoveries related to your research using the Index? Have you used the Index for teaching as well as for research?
I have never used the Index for teaching and, frankly, cannot remember a single eureka moment while using it (except, of course, finding a picture I did not know).
Have you attended or presented at an Index conference? Which conferences were particularly memorable or helpful to your work?
I gave papers at Iconography at the Crossroads2 and Romanesque Art.3 Both were very important gatherings and publications.

Do you have any observations about the evolution of the field of medieval iconographic studies over the last three decades?
As recently as twenty years ago, one of my own graduate students brushed away an argument with “That’s only iconography,” “Only” was the operative word there. In the wake of the material turn, decolonial turn, global turn, historiographic turn, experiential turn, the ornamental turn, . . . . , searching for texts that identify medieval subjects is no longer sufficient. And with the Patrologia Latina and other compendia online, it is not even fun. Simply to dismiss iconography, however, is ignorant. As I myself have argued at length in a recent essay, “the interweaving of text and image and the sensual pleasure of [medieval art’s] color and rich materials” was the essence of medieval art.4 Iconography is therefore destined to remain a fundamental instrument for studying it.

Please join us and register for the next virtual database tutorial with the Index on Tuesday, March 25, 2025 from 12:00 – 1:00 pm EST.
Read more about it at this link: https://ima.princeton.edu/index_training/.
The Index of Medieval Art is pleased to launch a new series of blog posts that delve into the history of the organization through interviews with senior scholars in the field of art history. The “Guest Book Series” takes its name from the Index guest books, which have been signed by scores of art historians who have consulted the Index files over the past century. We’ve enjoyed reading their recollections, and warmly thank our interviewees for their time and responses.
Please tell us a little about yourself and your work. Where did you study? What inspired you to become a medievalist?
I’m not a medievalist but my work in Renaissance iconography has always depended on research material from earlier times. I had my first course in art history as a senior in high school, Mary Institute, St. Louis, 1942–1943. I majored art history at Washington University, St. Louis, receiving my M.A. (1949) under H.W. Janson, and did graduate work at the Institute of Fine Art, NYU, with Erwin Panofsky and others. I received my PhD on the basis of three related published articles in 1973.
When was your first visit to the Index in Princeton? Where was the Index located then? With whom did you work there? Do you remember anything especially interesting about your visit?
My first visit to the Index was in 1950. For a seminar with Panofsky, I was investigating the sudden appearance of the Infant St. John the Baptist in the Florentine early fifteenth century. The Index was in McCormick Hall. I met Rosalie B. Green and worked with her and Isa Ragusa. I also, by chance, met Professor Morey on that visit. I quickly found that the arrangement of the Index card catalog did not offer simple searching under the Baptist’s name. Learning the biblical structure of the index then helped me broaden the conceptual basis of my project and enriched my results.
In my years of working in the Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana, it was always reassuring to know that the copy of the Index was there for consultation. In the 1980s, when I was a member of the Getty AHIP team, the precedence of the Index was a motivating factor in creating new computer tools for art historical research.
Have you made any great iconographic discoveries related to your research using the Index? Have you used the Index for teaching as well as for research?
I am told that my article on the iconography of the Infant St. John, published in 1955 in The Art Bulletin remains useful up to the present day.

Do you have any observations about the evolution of the Index files and database? Where do you think Index work should go next?
With the appointment of Pamela Patton, the Index has finally hit its stride. Along with its change of name, broadened constituency, and superb technical improvements, the Index is fast becoming a major research center. It seems to me obvious that these advances indicate that the direction The Index of Medieval Art is going is the right one.

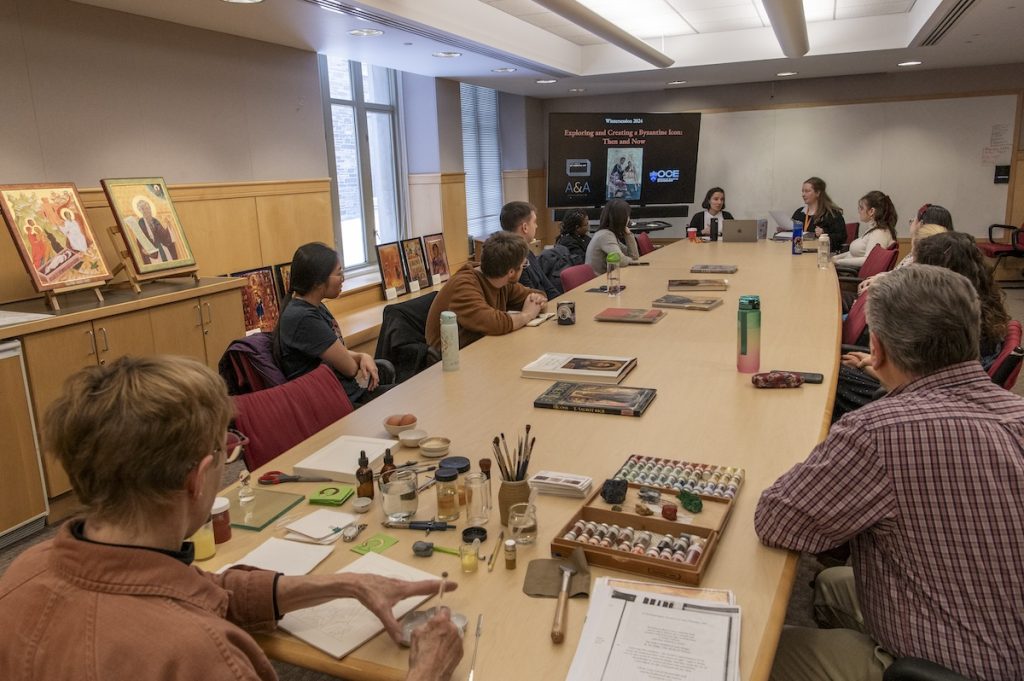
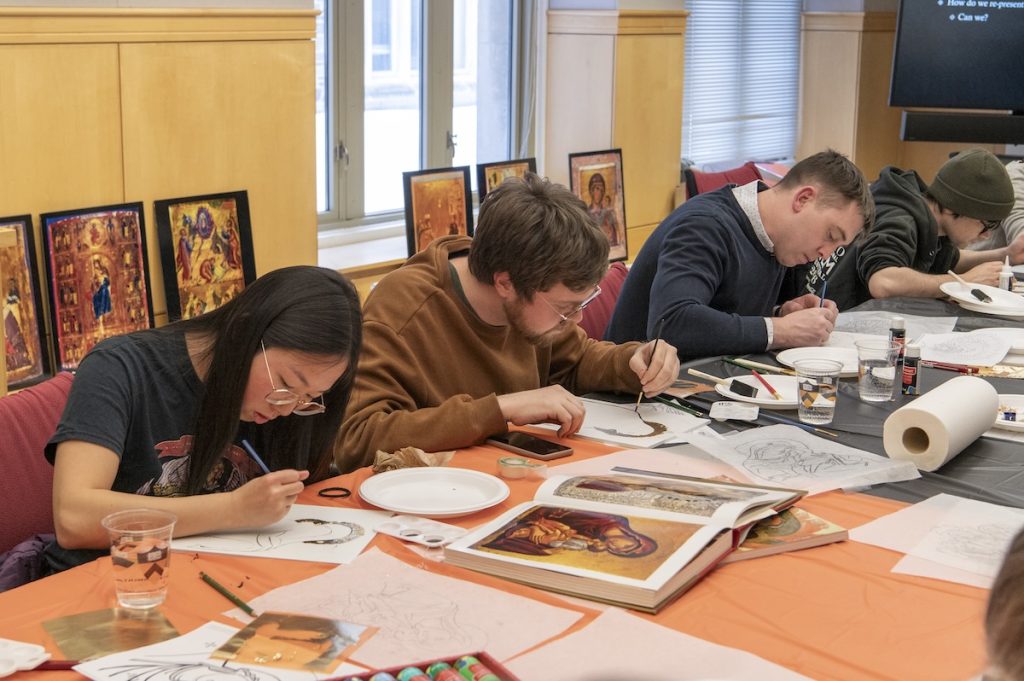
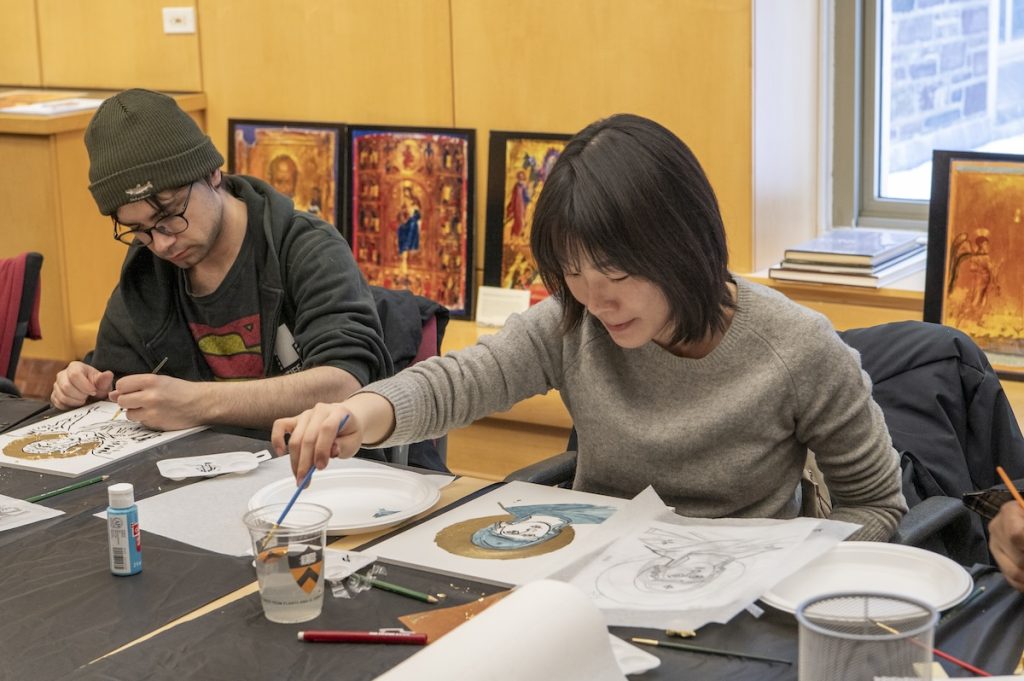
The Index of Medieval Art was delighted to offer its second Wintersession, “Exploring and Creating a Byzantine Icon: Then and Now,” on January 23rd, 2024. Its fifteen participants included Princeton staff, faculty, undergraduate and graduate students. In the first part of the workshop, they learned about the history and creation of Byzantine icons. In the second, they had the opportunity to create their own icons using modern artistic materials.
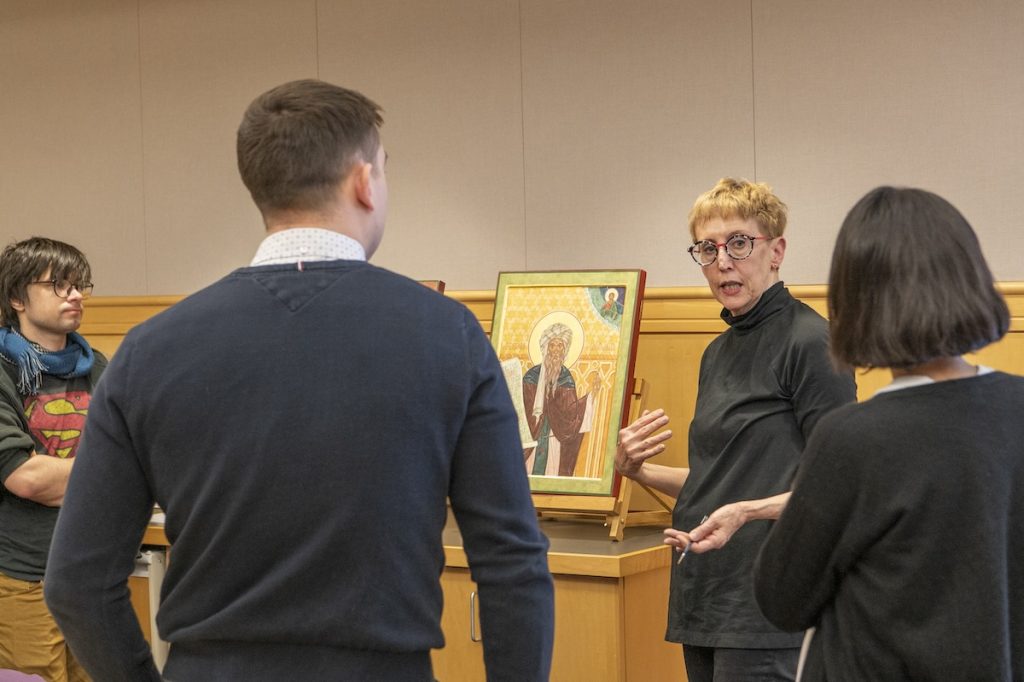
Index Art History Specialists Maria Alessia Rossi and Jessica Savage led the workshop, opening with a presentation on the Index resources and delving into some questions about iconography using large reproductions of the icons from Mount Sinai, generously loaned by Visual Resources, as a basis. The group discussed the iconographic details in works of art, exploring the subject matter in icons that generate tags in the Index database. Jessica invited the students to observe the figures and scene in a twelfth-century Sinai icon of the Annunciation (Index system no. 57527), looking for major and minor details in the painting, as small as an octopus swimming underwater. Alessia introduced participants to the way Byzantine icons were displayed and their devotional practices by examining a folio from the Hamilton Greek Psalter (Index system no. 103381).
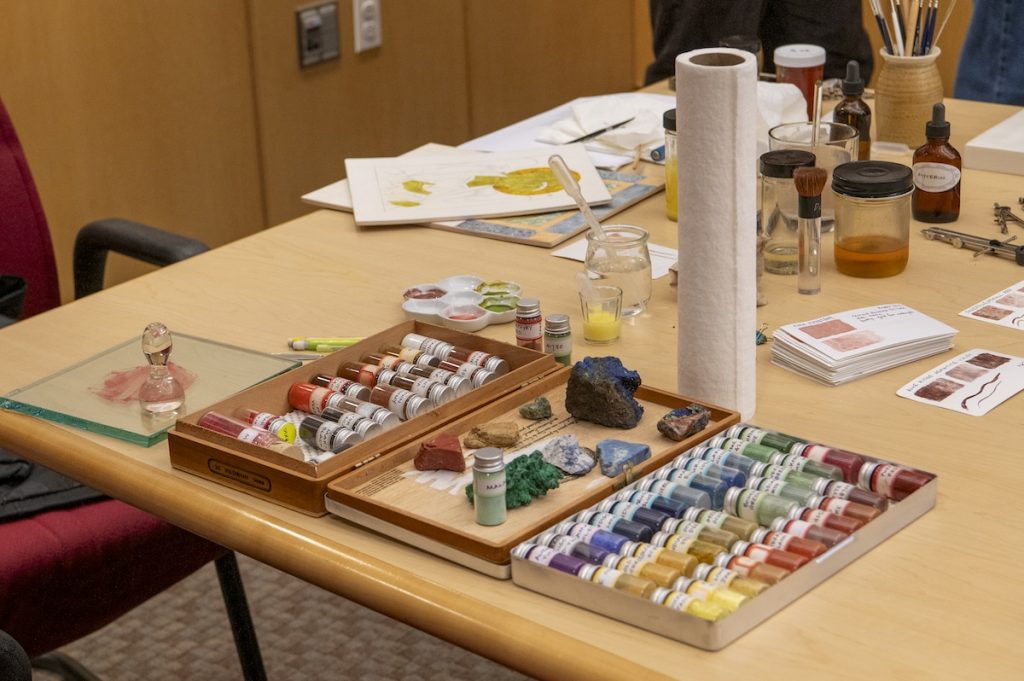
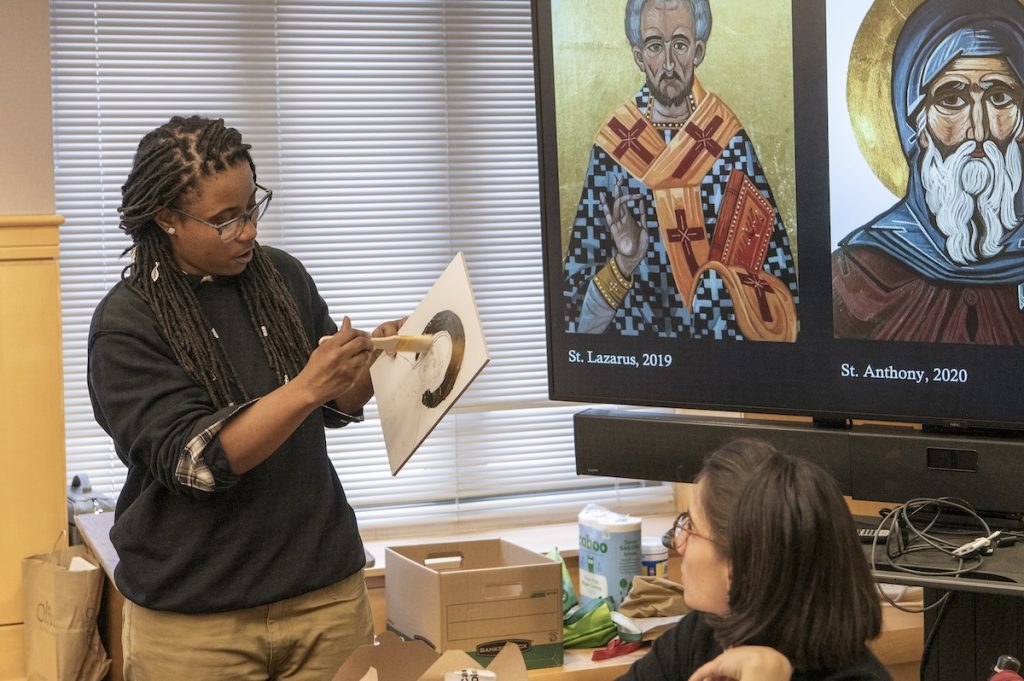
The first guest lecturer, local icon painter Maureen McCormick, showed the participants how to make the binder for egg tempera paint by mixing egg yolk and … No, not water … rather, white wine! Maureen showed the class all the tricks of the icon painter, including where to buy authentic pigments, how to grind them, and how to literally use one’s breath to “blow” gold leaf onto a red clay bole sample, which formed the nimbus of a saint. A short Instagram reel was made by Kirstin Ohrt, Communications Specialist in the Department of Art & Archaeology, to show Maureen’s breathtaking lesson in action, and you can check it out here: https://www.instagram.com/artandarchaeologyprinceton/reel/C2ud3gZLAJW/.
The afternoon session was led by Department of Art & Archaeology graduate student and icon painter, Megan Coates, who spoke about her own work with icons, as well as their importance for memory and communication. As part of an organized hands-on activity, participants created their own Byzantine icons using templates designed by Megan or choosing their own models from books or memory. Acrylic paint, brushes, drawing materials, gessoed panels, as well as gold and silver leaf materials were supplied by the Princeton Office of Campus Engagement. The outcomes were astonishing!
It was a pleasure to observe the participant’s ideas and skillful process unfold as they engaged in the long-treasured art of icon-making. One participant Sigrid Adriaenssens, Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering, wrote to us after Wintersession and said, “Thank you so much for organizing this workshop. It opened a whole new world to me that I didn’t know existed at Princeton. I really enjoyed learning about the Index, icons, and how they are made. The speakers Maureen and Megan were also very interesting and exciting to listen to!” Another participant, Zi (Zoe) Wang, visiting doctoral candidate and researcher at Princeton from the Central Academy of Fine Arts in Beijing, said she felt transported by the instrumental music we played during the hands-on activity. Zoe said about the experience, it was like “immersing myself in meditation.” We couldn’t agree more!






Are you interested in learning more and researching icons at the Index? Here are some general tips for starting an Index search about Byzantine icons, especially if you do not know exactly which icon you are looking for!
However, these results might be too broad, so if you want to refine them you can keyword search the word “Byzantine” on the upper right search window of the database, and then filter by these other controlled terms we just mentioned, such as Work of Art Type “panel” or Medium “wood.” But if you want even narrower results, or if you know the iconography you are interested in, such as the iconography of an angel, or searching for angels by name, as in the case with the Annunciation image, you can filter by the Subject “Gabriel the Archangel.”
If you have any questions about starting research with the Index resources, fill out our inquiry form and we will be in touch: https://ima.princeton.edu/research-inquiries/.
Finally, this Wintersession workshop could not have been possible without the generous support of the Princeton Office of Campus Engagement, the Department of Art & Archaeology, and the Index of Medieval Art. Thank you to all who helped plan and participated in this event!
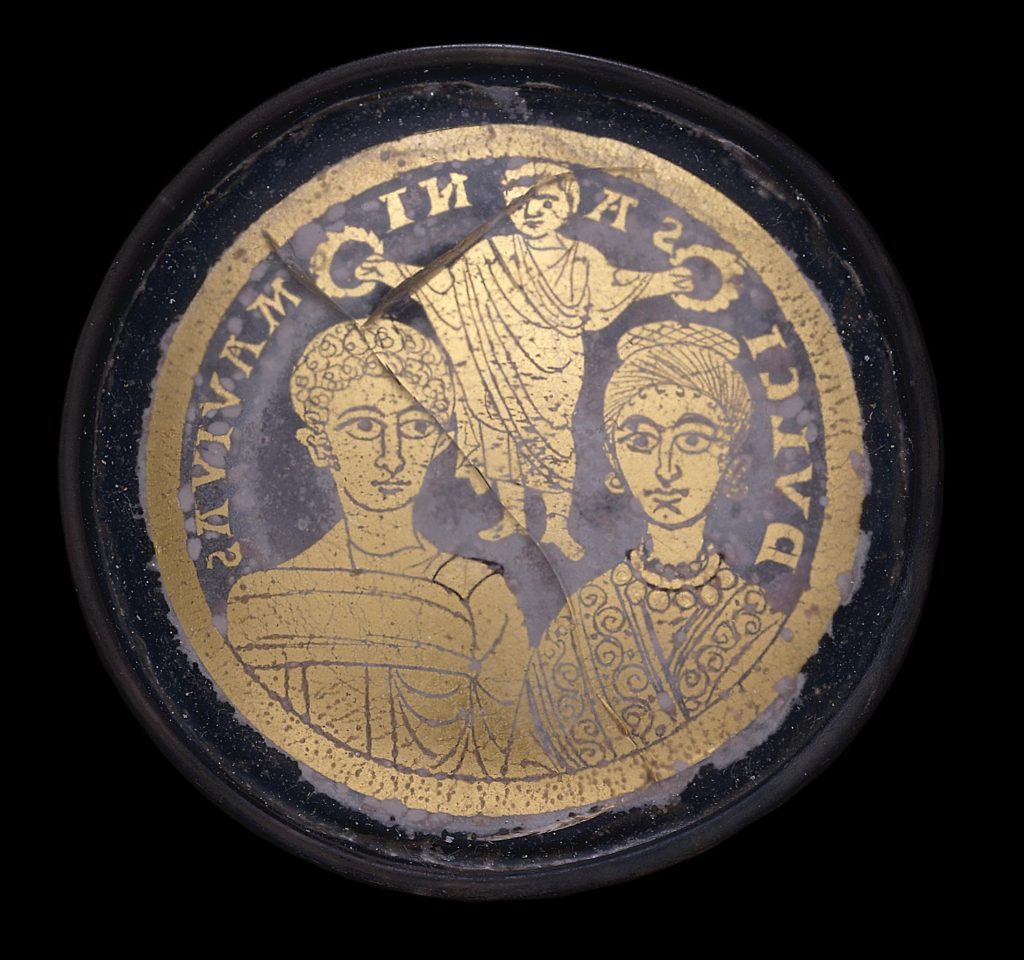
As editorial staff at the Index continue cataloging our physical backfiles, which contain over 200,000 photographs of works of art in sixteen media categories, we are happy to announce that at last, all our print records of gold glass objects have been fully digitized in the Index database! In gold glass, an image in gold leaf is fused between layers of glass. Gold glass was a favored art form in Hellenistic Greece and during the Roman period, often decorating the bases of feasting vessels, such as bowls, cups, and plates, with hidden pictures that would slowly be revealed during the consumption of food and wine. The newly digitized “Gold Glass” backfiles document over 650 objects from about 60 locations. Most examples are identified as vessels, medallions, or plaques (Fig. 1).
The glittering portraits on these glass objects, now mostly fragmentary, are usually bust length and often show whole families. These are classified under the Index subject “Family Group,” while the subject “Married Pair” is used for images depicting a bride and groom, sometimes crowned by Christ. Gold glass objects are frequently associated with marriage celebrations, and several pieces retain the names of the men and women depicted with inscriptions of good wishes. Frequently, this inscription is the Latin drinking toast “PIE ZESES” (“Drink to live,”), either in full or abbreviated, although a fourth-century gold glass fragment from Rome, now in the British Museum, bears the more sentimental words “DVLCIS ANIMA VIVAS” (“Sweet soul, may you live [long]”) around the heads of the newlyweds (Fig. 2).

Several gold glass objects contain other paired figures, especially Peter and Paul the Apostles, as the patron saints of Rome, and Adam and Eve, commonly represented in the Fall of Man scene. Old Testament narratives and figures, such as Moses, Abraham, Daniel, and Jonah were popular, and Christian miracles were also frequently depicted on vessels. The Index database contains just over fifty miracle scenes executed in the gold glass medium, including the Raising of Lazarus, the Miracle of Loaves, and the Wedding at Cana, suggesting that healing themes held some favor among patrons. The objects may also have served a commemorative function.
Some surviving gold glass objects contain Jewish iconographic motifs, including the Temple implements, such as the menorah, shofar, etrog, and Torah Ark. These implements can be found in the Index database by browsing the Subject list, or by searching for “gold glass” as a term and filtering by the Style/Culture “Jewish.” Mythological figures and narratives from the classical world were also favored subjects to depict on gold glass vessels. The Herculean labors, sea-nymphs, and cupids can be identified on some fragments. Other well-represented motifs in the medium include the “Good Shepherd,” which has iconographic connections to the ancient Greek ram-bearing cult figure Kriophoros. There remains much to discover and assess about images in gold glass and their meanings, production, and patronage throughout the late antique, Roman, and Byzantine periods, making the Index an essential study tool. Now, with increased access, more researchers can learn how this rather fragile art form documents fashion, commerce, rituals, and historical names and epigraphs from ancient daily life (Fig. 3).
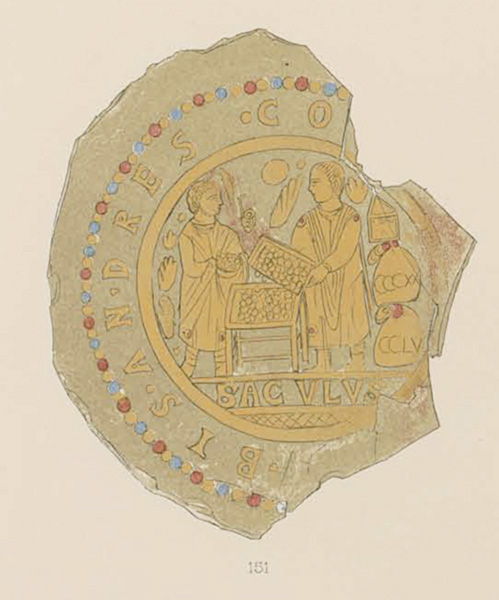

The Index gold glass backfiles received significant attention by Ryan Gerber, our 2019 summer intern from the Rutgers School of Communication, who is now a Marquand Art Library Collections Specialist. Gerber inventoried the collection and wrote about his impressions in a blog post called “A Face in Gold Glass.” After Henry D. Schilb, Index Art History Specialist in Byzantine Art, finished adding the collection with the help of Gerber’s inventory, he noted that many gold glass objects recorded in major nineteenth century catalogs did not survive into the modern era. Thus, the publications that earlier Index catalogers used in their research may have contained the last known record of an object’s existence. Schilb said, “it was surprising to learn that many of the gold glass objects entered into the Index files have been lost to time, and at least one of them was apparently reduced to dust in the collection where it was last recorded. Not surprisingly, we have also simply lost track of several examples that were originally cataloged by Indexers before the Second World War.” With too little information to go on, the Index cataloger can sometimes upload only a drawing from the catalog and record only a “Last Known Location” for objects presumed lost to history. When we just don’t know where something is, we indicate this in the database by giving “Unknown” as the current location with a “Last Known Location” to identify the place where an item was last known to exist. This can apply to items that we know to have been destroyed, but it also applies frequently to items that are either simply lost or are now in unidentified, private collections. Although the Index can sometimes discover an object’s true current location, that bit of data can sometimes elude us, so we always welcome intelligence from anyone who might have a good lead!
It is a great achievement when we can complete an entire category in the backfiles with newly researched information, including updated location names, fuller iconographic descriptions, and new or updated terms from Index vocabularies to expand the findability of work of art records. We ought to be clear, however, that we do not claim to have recorded every known example of any medium or type of object. That must remain an ongoing project. Nevertheless, the whole Index team is thrilled to make the gold glass corpus of the original Index card catalog fully available in the database. If you want to see for yourself, you can browse “gold glass” records by Medium more fully here: https://theindex.princeton.edu/s/list/ListMediums.action. You can also reach out to us with any inquiry here: https://ima.princeton.edu/research-inquiries/. Please let us know how the Index can improve the records we have, or find out how the Index can serve your own research needs.
Cheers!
Further Resources
Garrucci, Raffaele. Vetri ornati di figure in oro: Trovati nei cimiteri dei cristiani primitivi di roma. Rome: Tipografia Salviucci, 1858.
Deville, Achille. Histoire de l’art de la verrerie dans l’antiquité. Paris: Morel, 1871.
Vopel, Hermann. Die Altchristlichen Goldgläser: Ein Beitrag zur altchristlichen Kunst- und Kulturgeschichte. Freiburg im Breisgau: J. C. B. Mohr, 1899.
Morey, Charles Rufus. The Gold-Glass Collection of the Vatican Library: With Additional Catalogues of Other Gold-Glass Collections, ed. Guy Ferrari. Vatican City: Biblioteca apostolica vaticana, 1959.
Meek, Andrew. New Light on Old Glass: Recent Research on Byzantine Mosaics and Glass. London: British Museum Press, 2013.
Howells, Daniel Thomas. A Catalogue of the Late Antique Gold Glass in the British Museum. London, British Museum Press, 2015.

We are excited to announce a short-term graduate opportunity at the Index of Medieval Art! This is a two to three-month remote, part-time research opportunity to help incorporate key works of art on Mount Athos into the Index database. The position would require the student to examine the Index legacy records, update the metadata, identify new color images, and incorporate them into the online database. They will be trained in Index norms in cataloging works of art, describing the iconography, transcribing inscriptions, and adding bibliographic citations.
The position is part of a new multi-year project, Connecting Histories: The Princeton and Mount Athos Legacy, that aims to create an international team of faculty, staff, and students that will explore and bring awareness to the rich, complex, and remarkable historical and cultural heritage of Mount Athos, and its connection to Princeton. This opportunity offers a stipend of $2,500 and has been generously funded by the Seeger Center for Hellenic Studies, with the support of the Dimitrios and Kalliopi Monoyios Modern Greek Studies Fund and Art & Archaeology Department at Princeton University.
The deadline for applications is December 1, 2023. For more details about eligibility criteria and the application process, please visit the “Announcements” page on the Connecting Histories website.
We are excited to announce that the mosaics of St. Sophia Cathedral in Kyiv are now live in the Index database! Thanks to a Flash Grant from the Princeton University Humanities Council, Dr. Julia Matveyeva, Associate Professor in the Department of Fine Arts and Design of the O. M. Beketov National University of Urban Economy in Kharkiv, joined the Index remotely for the last five months to work on Ukraine’s medieval cultural heritage. Find out more about St. Sophia Cathedral, the work of an Index cataloger, and Dr. Matveyeva’s research at this link.
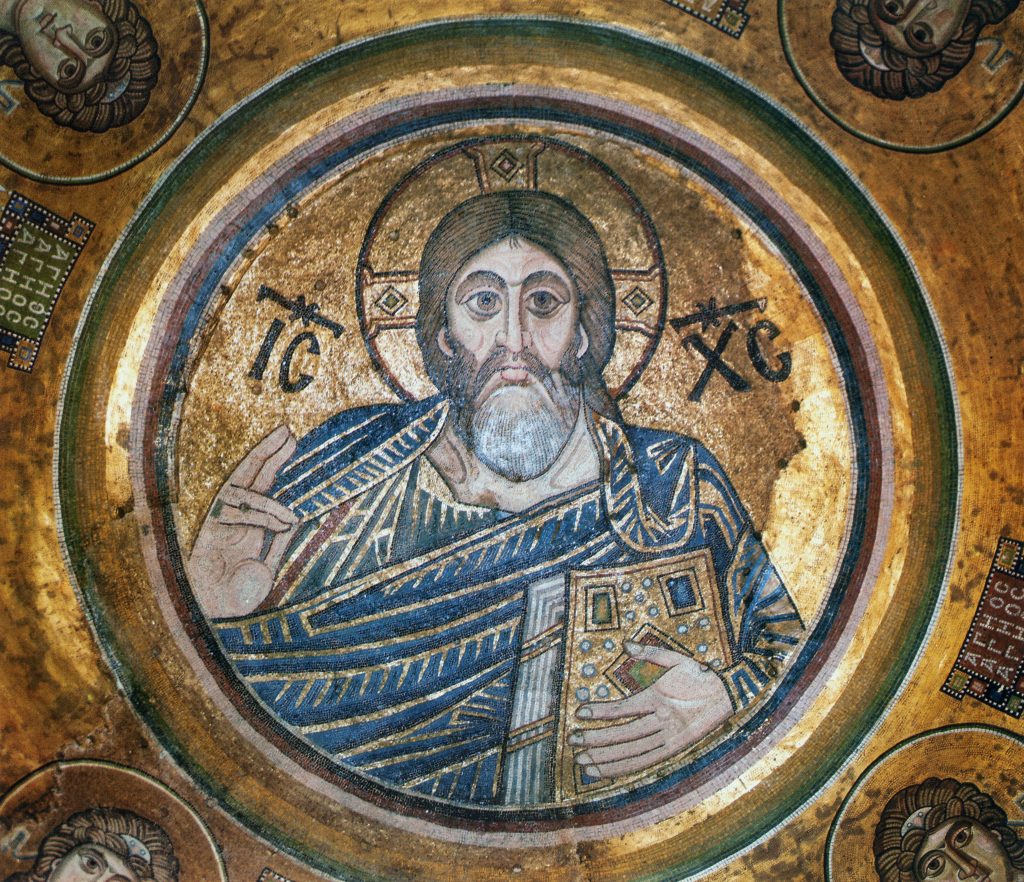


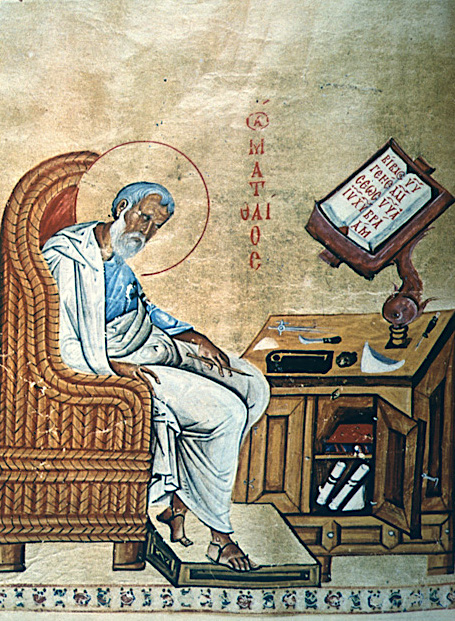
As the fall 2020 semester begins and the Index staff continue to work remotely, each of us connecting from different locations, our home libraries and desks have become essential tools in our research. They call to mind medieval images in which the scribe’s desk and well-stacked bookshelves are familiar iconographic attributes of the Evangelists, as well as theologians, scholars, physicians, and literati, as they labored in their study spaces (see Index subjects: Bookcase, Scholar, Physician, Literatus, and Philosopher Type). Their desks took a variety of forms and shapes, from tall book stands or lecterns, sometimes decorated with animals, birds, and foliage, to round or squat tables of a simpler design. Medieval images of scribes and writers often show the surfaces of their desks covered with open books or sheets, some with scrawled lines (search Index keyword: pseudo-inscriptions), inkhorns and inkpots, knives, pen cases, and a spare stylus or two.


Working in a modern study space, many of these similar tools are within my reach: pens, scissors, a pencil cup, and plenty of Post-it Notes containing my jotted reminders—arguably legible! My computer desktop is a hub for images of medieval works of art, articles, and spreadsheets that help organize my Index work. To the right of me, sits a modest collection of tomes (to name a few, Emile Mâle’s Religious Art in France: The Late Middle Ages; Roger Wieck’s Painted Prayers: The Book of Hours in Medieval and Renaissance Art; Baxter’s Bestiaries and Their Users in the Middle Ages, and the catalogues The Splendor of the Word and The Golden Age of Ivory Gothic Carvings in North American Collections). Some books are my own and some are out on temporary loan from the Index’s research library and from Firestone Library, but all are bolstering this new environment of cataloguing and scholarship from home.
For Index research staff, this means that our working desktops (both physical and virtual) and our carefully curated home libraries (whether lining our walls or nested digitally into desktop folders) will support our ongoing remote activities. This semester, we will continue to pursue new art historical research for additions to the database, including works from the original print backfiles, from monumental mosaics to illuminated manuscripts and ivory objects. We remain focused on expanding the Index collection to present the rich array of iconography from the global Middle Ages. We will also continue to refine the database by building and improving work of art location authorities, further developing Index subject classifications that improve thematic browsing, and implementing the new hierarchical browse tool for researching the placement of medieval iconography within structures. Above all, we will remain available to support researchers at all levels in their use of the online Index database.
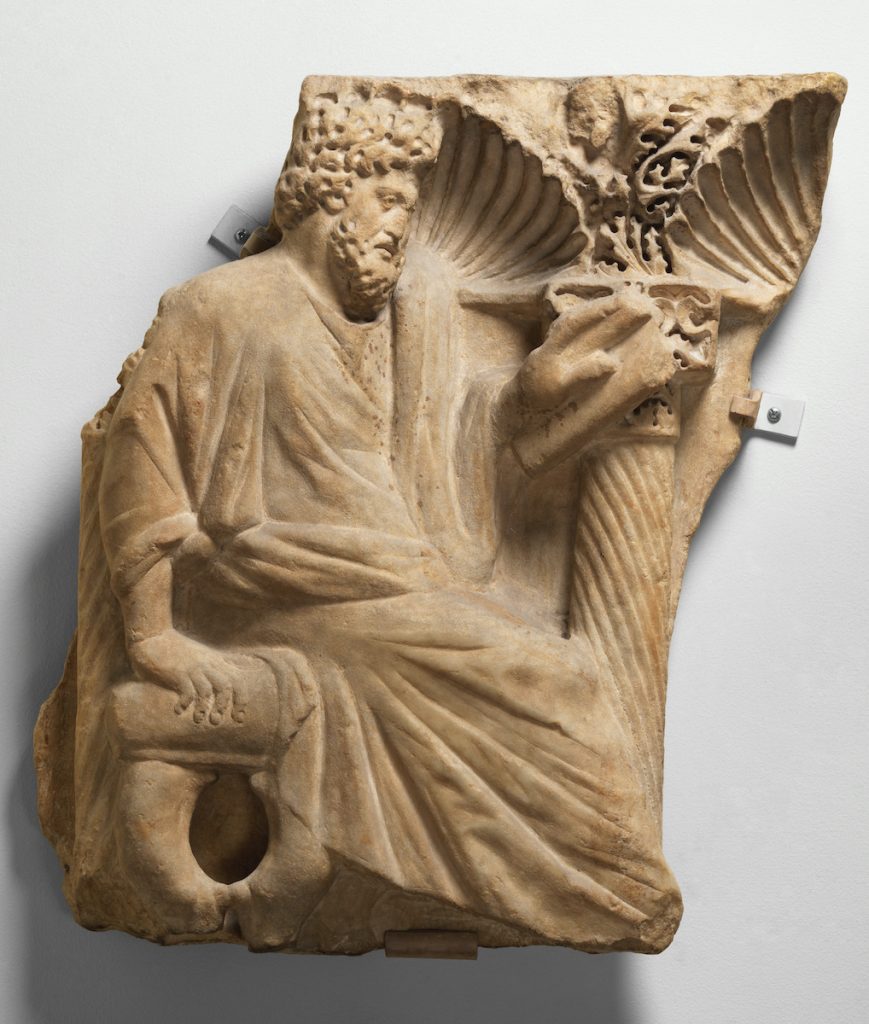


Wherever you may be this term—whether you feel like a monk in a cell or a monkey with an inkpot—we hope that you are well and looking forward to your study, surrounded by the tools of your scholarship. We look forward to hearing how we can help serve your research and teaching in the upcoming academic year.
