

Someone made each of the works of art described in the Index of Medieval Art, and since the beginning of its online database, The Index has acknowledged the individuals and workshops responsible for generating illuminated manuscripts, sculptures, mosaics, et al. when their identities are known. In the original Index system, artists and scribes each occupied a separate field, however, in the updated Index a new field has been established to incorporate both roles under the title of Creator. This reflects the fact that in some media, such as manuscript illumination, the roles of scribe and artist were not always separate: at times one individual undertook both kinds of work, while in other cases the jobs were more specialized.
The Index here expresses a caveat: Creator will not appear on every record. Medieval artists and scribes were/are largely anonymous, creating unsigned works of art for patrons who were also frequently unknown. However, some of the approximately 1400 creators who are named in the Index are known because they signed their works. Others were acknowledged by patrons who named artisans in their inventories, and still others have been identified by modern art historians who have spotted enough similarities among groups of works to assign a nickname for their otherwise anonymous master.
You can learn more about the artist associated with a particular work of art by looking at the work of art record, where the Creator field is located just toward the bottom. In the example below, a screen shot of a manuscript main record shows the name of Simon Bening as creator.
Click on the name, and another window will open providing information about the creator, including such information as general notes, alternate names, bibliographical citations, profession/s and work of art references. This last bit of information presents a list of all works of art associated by the Index with the artist. In the case of our example Simon Bening, this includes some 250 manuscript folios attributed to the artist and included in our database. The researcher can then click through the records to view these works.
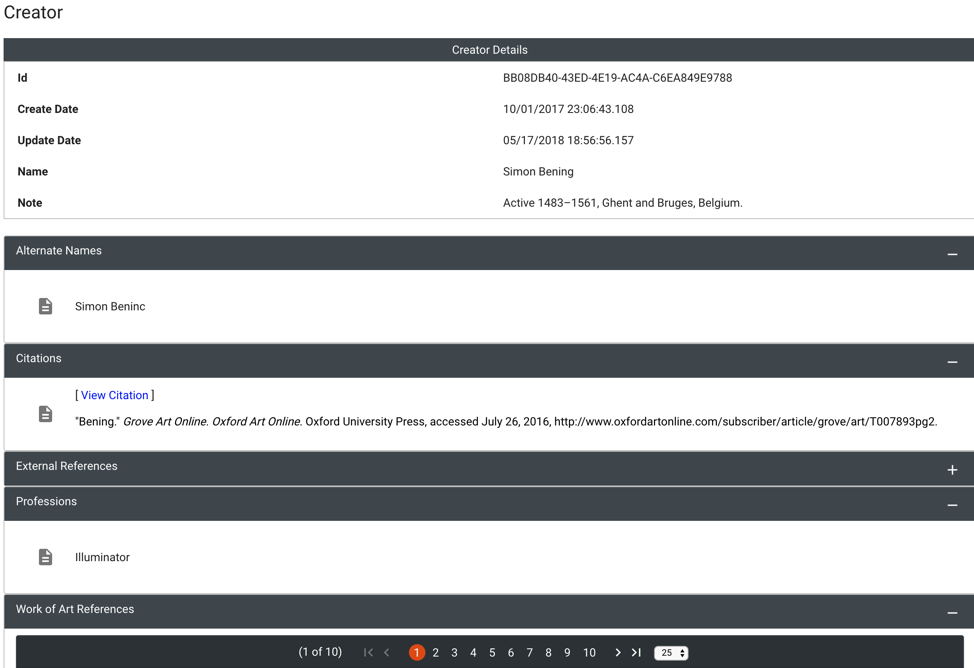
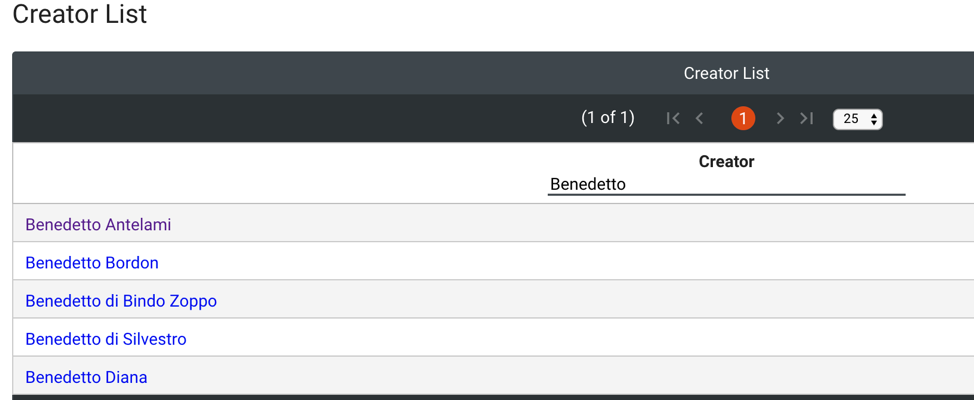
You can also browse by Creator name to see the information and records that the Index includes for a particular Creator. Choose the Browse option on the home page, and from the Browse Indices, click on Creator to open an alphabetical list of names. To find the artist or scribe of interest, either scroll through the list or type the desired name on the line below “Creator” at the top of the list. Click on the correct name, and a window will open as above.
The information about artists and scribes is intended to provide a springboard for further research. Citations frequently include an article in Oxford Art Online, many of which are followed in turn by relevant bibliography.
Although as noted, most medieval artists and scribes are unknown, The Index does include nearly 1400 “named” creators. A significant portion remain personally anonymous, but have been given monikers based on the attribution of works of very similar style or other details, such as the Gold Scrolls Group, named for a distinctive style of ornament, or the Master of Catherine of Cleves, a name based on work created for a specific patron. Searching Grove Art Online for “Anonymous Masters” will yield page after page of unknown creators whose works have been linked in this way to create a body of work by one artist, scribe or workshop. Because many of these names are still in use in art historical scholarship, the Index includes them in the Creator list, sometimes designating them as “see from” terms when consensus about authorship is not clear. We love to keep our records updated, so if you know of new research about the attribution of a work of art, please bring it to our attention at theindex@princeton.edu.
Judith K. Golden